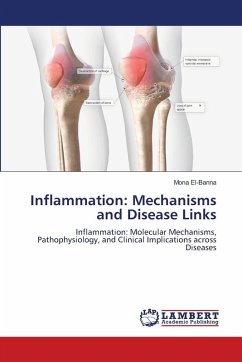
Inflammation is a coordinated biological response to pathogens, tissue damage, or environmental stressors, involving immune and non-immune cells, signaling pathways, and soluble mediators to restore homeostasis. Acute inflammation is protective, marked by rapid innate immune activation, leukocyte recruitment, and cytokine release (TNF- , IL-1beta, IL-6), with NF- B, MAPK, and JAK/STAT pathways driving gene transcription. Resolution occurs via pro-resolving lipid mediators, anti-inflammatory cytokines, and clearance of apoptotic cells. Dysregulation leads to chronic inflammation, driving autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disorders, metabolic syndromes, cancers, and neurodegeneration. In CVD, vascular inflammation induces endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis; in metabolic disease, low-grade inflammation promotes insulin resistance and NAFLD; in cancer, it fosters genomic instability and immune evasion. Neuroinflammation, mediated by microglia and astrocytes, contributes toAlzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis. Understanding these mechanisms enables targeted therapies that suppress pathological inflammation while preserving protective functions.
Bitte wählen Sie Ihr Anliegen aus.
Rechnungen
Retourenschein anfordern
Bestellstatus
Storno